Lipedema
Lipedema is often confused with obesity, so losing weight is not very promising. Lipedema is a disease of which, unfortunately, very little is known even today. It is well known that a certain predisposition is required, which can often lead to an unproportional increase in fat tissue in the legs or arms after puberty or pregnancy. Typically, in addition to the increase in volume and circumference, there is an increased painfulness and tendency to bruises. While at the beginning the lymph drainage is increased, it can decrease in the course and secondary lymphedema can develop. Unfortunately, the progression of lipedema is triggered by additional overweight.
According to the current guidelines for lipedema, conservative measures such as wearing medical compression stockings/ trousers, manual lymphatic drainage, weight reduction and physical activity are available. Liposuction can reduce fat tissue and often pain, but not cure predisposition and disease. Even after liposuction, conservative measures should be continued. In many cases, however, the intensity is reduced. Essential for the success of the application regarding the assumption of costs is a) the stage of the disease, b) the conservative treatments carried out according to guidelines (under medical control and supervision with corresponding documentation).
Picture: Edema therapy Vodder
Disease: Lipedema is a disease that occurs only in women. It manifests itself in the form of disproportionately thick legs with often slender trunks. The marked increase in fat in the legs usually occurs during puberty or after pregnancy. Although the cause is not known, hormones and heredity seem to play a role.
Complaints: In addition to an overall disproportionate figure, there is a feeling of tension and heaviness on the upper and lower legs as well as a pronounced feeling of touch and pressure pain. This is the result of water retention (edema) in the increased fatty tissue, especially in the evening, after long periods of standing and in warm weather. A further symptom is bruising ("bruises"), which occur even after minor blows.
Location: Lipedema is usually found in the buttocks and thighs, but can also extend from the knees or to the ankles. The feet are usually not swollen.
Course: In many patients, the findings become worse over the course of their lives. While the subcutaneous fatty tissue is initially evenly soft, palpable knots appear in the course of time and the tissue becomes firmer. In late stages, overhanging fat flaps on the inside of the thighs and knees can hinder walking.
Previous treatment: Diets, sports and drainage tablets do not improve the situation. Up to now, edema could only be removed from the legs with decongestion treatments in the form of manual or apparatus lymphatic drainage, gymnastics and compression stockings.
is called "complex physical decongestion therapy" (KPE). This improves the symptoms but does not eliminate the increase in fat that causes them. These measures must be carried out for the rest of one's life.
Modern treatment: In recent years, liposuction (liposuction) has for the first time made possible a largely causal treatment. The development of new local anaesthesia methods (tumescent local anaesthesia) and new suction techniques (vibration liposuction) with thin and blunt micro probes have revolutionised the treatment of lipoedema. By eliminating the increased fat volume, not only is the appearance normalized again, but the physical and psychological complaints caused by this are also completely or predominantly eliminated. In many cases a decongestion treatment is still necessary, but to a limited extent. Also when wearing compression stockings, a lower compression class can usually be used.
How often is surgery performed? Depending on the extent of the findings, one or two, rarely three operations may be necessary. These can be performed at intervals of several weeks. Already after the first operation a clear improvement can be noticed.
Costs: Unfortunately, the costs of the operation are not covered by the statutory health insurance. Liposuction usually has to be paid for by the patient.
diagnostic
manifestations of lipedema:
Type I: fat tissue proliferation in the buttocks and hips (horsehose phenomenon)
Type II: Lipedema extends to the knees, fat flap formation in the area of the inside of the knee
Type III: Lipedema extends from hips to ankles
Type IV: arms and legs are affected
Type V: Lipolymphedema.
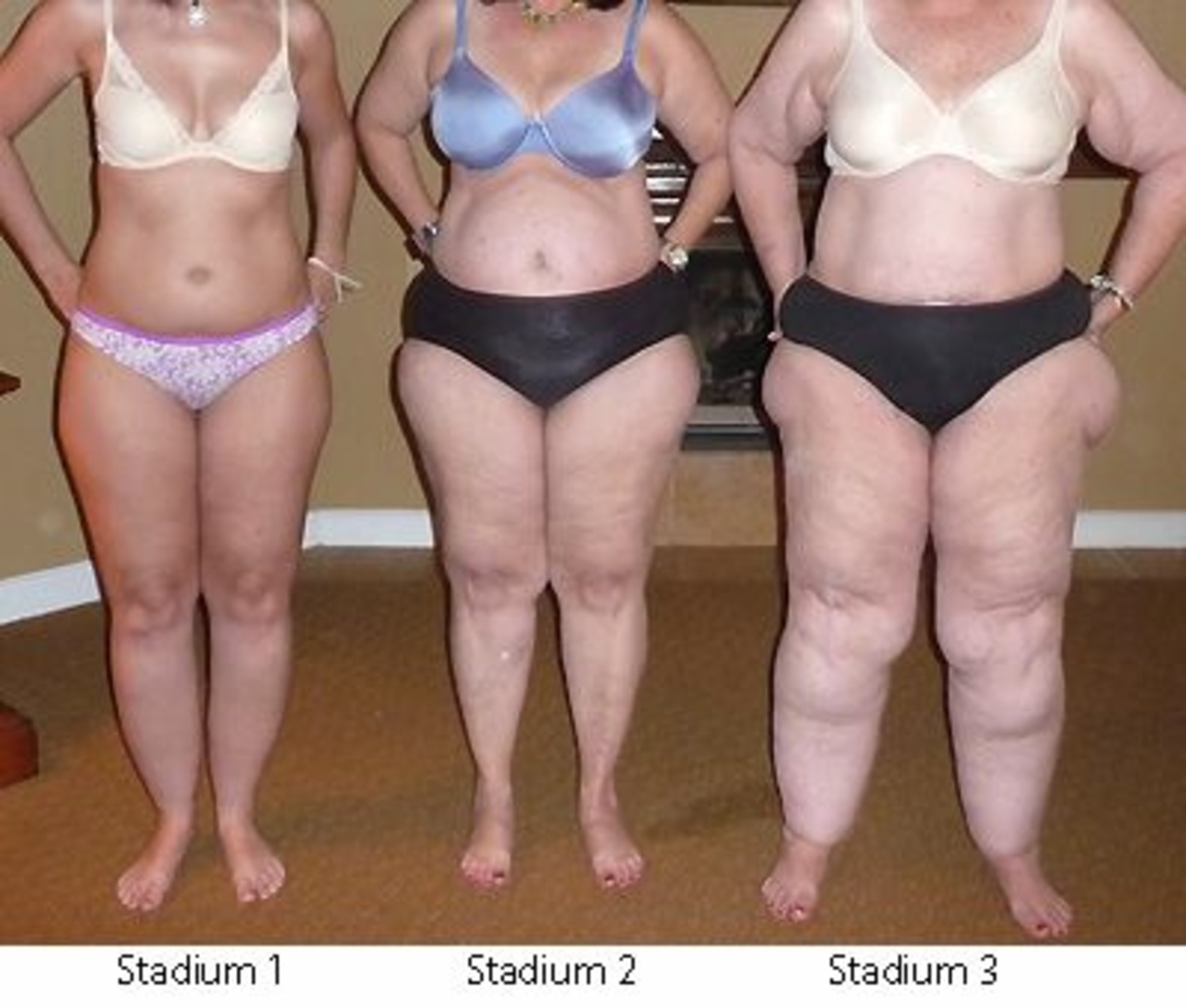
Depending on the severity of the disease we divide it into stages.
Stage 1: Orange peel skin, fine nodular skin surface
Stage 2: Mattress skin, coarse skin surface with larger dents
Stage 3: coarse, deforming fat flaps
General diagnostics: In most cases the diagnosis is to be made by anamnesis, inspection and palpation. Lipedema

we can see only from the way we look and touch it.
The typical distribution pattern of the fat pads on hips, thighs, knees
and in the ankle region as well as the absence of the feet indicate lipedema. Orthostatic edema occurs in the second half of the day. The pain caused by touching or pressing the front edge of the shinbone also indicates lipedema.
Special diagnostics - plethysmography: The arterial reserve is limited because even the smallest arteries can no longer circulate the subcutaneous fatty tissue well in this coarse, solid fatty tissue.
Sonography (Marshall): Sonography of the lower extremities shows an even distribution of the subcutaneous fat tissue with a snow flurry-like change of the subcutaneous fat tissue.
- indirect lymphography
- flame-shaped injection depot (K.U.Tiedjen)
- Functional lymph scintigraphy (according to Weissleder)
It is a scintigraphy in which the recording of the particles in the lymph nodes is measured according to a predetermined motion sequence. This examination method can be used to determine whether an accompanying lymphedema is already present.
Computer tomography: Shows a clear thickening in the subcutaneous fatty tissue as well as in the nuclear spin examination.
Fluorescence microlymphography: Typical changes in the lymph capillaries with aneurysm-like bulges (vesti)
Pressure pain measurement: At fixed points of the limb the pressure-algometry (Reißhauer) takes place.
Text translation with software